The Difference between Quick and Slow EV Charging: Unravelling the Enigma of Batteries!
Electric vehicles are quickly becoming the future of transportation, and one of the big questions for EV owners is how to charge their batteries. Knowing the difference between quick and slow charging can help make the most of your battery’s life and range. Quick charging is a great option when you need a full charge in a hurry, while slow charging is a great way to keep your battery topped up and healthy. Understanding the differences between these two methods can help you make smart decisions about when to charge your EV.
- Introduction
When it comes to electric vehicles (EVs), one of the most important factors to consider is the charging time. While some EVs can be charged quickly, others require a longer charging time. This difference in charging time can be attributed to the type of charging method used. There are two main types of charging methods: quick charging and slow charging. Quick charging is a fast and convenient way to charge an EV, but it can also have a negative impact on the battery life. Slow charging, on the other hand, is a slower but more gentle way to charge an EV, which can help to extend the battery life. In this blog article, we will be discussing the difference between quick and slow EV charging and how it affects the battery life. We will also be exploring the different types of EV batteries and how they impact the charging process. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of the enigma of batteries and the importance of choosing the right charging method for your EV.
- Background on EV Charging Technology
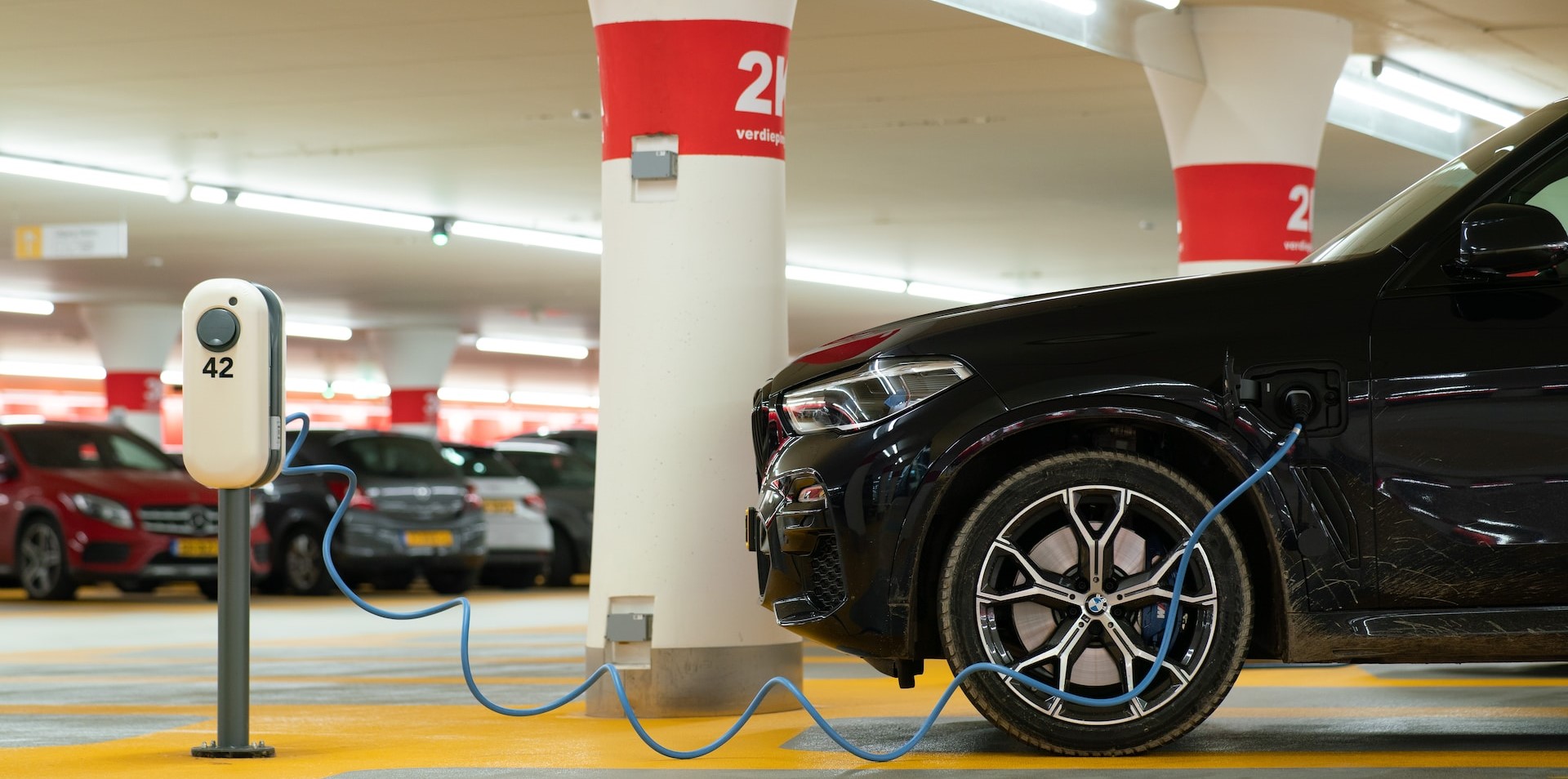
To fully understand the difference between quick and slow EV charging, it’s important to have a background on the technology behind EV charging. Electric vehicle charging technology has evolved significantly over the past decade, with advancements in both hardware and software. The most common types of EV charging are Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 (also known as DC fast charging). Level 1 charging uses a standard 120-volt outlet and is the slowest charging option, typically taking 8-12 hours to fully charge an EV. Level 2 charging uses a 240-volt outlet and can charge an EV in 4-6 hours. Level 3 charging is the fastest option, using a high-powered DC charger to charge an EV in as little as 30 minutes. However, Level 3 charging requires specialized equipment and is not yet widely available. As the popularity of EVs continues to grow, so too will the demand for faster and more efficient charging options. It’s important for consumers to understand the different charging options and their capabilities in order to make informed decisions about their EV charging needs.
- Benefits of Quick vs Slow EV Charging
When it comes to charging electric vehicles, there are two main options: quick and slow charging. While both have their advantages, quick charging is the clear winner for those who want to save time and get back on the road as soon as possible. Quick charging can take as little as 30 minutes to charge an EV battery to 80%, whereas slow charging can take several hours. This means that quick charging is ideal for those who are on the go and need to charge their vehicle quickly. Additionally, quick charging is more efficient than slow charging, as it uses a higher voltage and amperage to charge the battery faster. This means that quick charging can actually be better for the battery’s health, as it reduces the time that the battery is exposed to heat and stress. Overall, while slow charging may be more convenient for those who have time to spare, quick charging is the way to go for those who want to get back on the road as quickly and efficiently as possible.
- Understanding the Different Types of EV Charging Connectors
As electric vehicles become increasingly popular, it’s important to understand the different types of EV charging connectors. There are several types of connectors, including CCS, CHAdeMO, Tesla, and Type 2. Each connector has its own unique characteristics and charging speed, so it’s important to choose the right one for your needs. CCS and CHAdeMO are commonly used for fast charging, while Type 2 is used for slower charging. Tesla connectors are specific to Tesla vehicles and can only be used with Tesla charging stations. Understanding the different types of connectors can help you make informed decisions about where to charge your electric vehicle and how long it will take to charge. Additionally, it’s important to note that not all charging stations have all types of connectors, so it’s important to plan ahead and know which connectors are available at your destination. By understanding the different types of EV charging connectors, you can make the most of your electric vehicle and ensure that you’re always able to charge up when you need to.
- Exploring the Differences between Quick and Slow EV Chargers
If you are an electric vehicle owner, then you must be familiar with the terms “quick” and “slow” EV chargers. But have you ever wondered what the difference between the two is? Quick EV chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, can charge your EV battery up to 80% in just 30 minutes, while slow EV chargers, also known as Level 2 chargers, can take up to 8 hours to fully charge your battery. But why the huge difference in charging time? The answer lies in the charging technology used by both types of chargers. Quick EV chargers use direct current (DC) to charge your battery, while slow EV chargers use alternating current (AC). DC charging bypasses the onboard charger in your EV and directly charges the battery, resulting in a faster charging time. On the other hand, AC charging relies on the onboard charger to convert the AC power from the charger to DC power for your battery, which takes more time. So, which one should you choose? It depends on your needs. If you are in a hurry and need to quickly charge your EV, then a quick EV charger is the way to go. However, if you have time to spare and want to save money on charging costs, then a slow EV charger is a better option. Ultimately, the choice is yours, but understanding the differences between quick and slow EV chargers can help you make an informed decision.
- Pros and Cons of Quick and Slow EV Chargers
When it comes to EV charging, quick and slow chargers have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Quick chargers, also known as DC fast chargers, can charge an EV battery up to 80% in just 30 minutes, making them a convenient option for drivers who are always on the go. However, quick chargers are expensive to install and can put a lot of strain on the battery, reducing its lifespan over time. On the other hand, slow chargers, also known as Level 2 chargers, take longer to charge an EV battery but are less expensive to install and are gentler on the battery. They are also more widely available, making them a practical option for drivers who don’t have access to a quick charger. Ultimately, the choice between quick and slow chargers depends on the driver’s needs and circumstances. If you’re always on the go and need to charge your EV quickly, a quick charger might be the better option. However, if you have more time and want to preserve your battery’s lifespan, a slow charger might be the way to go.
- What to Consider When Choosing a Type of EV Charger for your Vehicle
When it comes to choosing an EV charger for your vehicle, there are a few important factors to consider. First and foremost, you’ll want to think about the charging speed that you need. If you’re looking for a quick charge, you’ll want to opt for a fast charger that can provide a high level of power in a short amount of time. On the other hand, if you’re looking for a more affordable option or don’t need to charge your vehicle quickly, a slower charger may be a better fit. Additionally, you’ll want to consider the type of charger that your vehicle is compatible with. Some vehicles may only be able to use certain types of chargers, so it’s important to do your research and make sure that you’re choosing a charger that will work with your vehicle. Finally, you’ll want to think about the location of your charger and whether you’ll need to install it indoors or outdoors. By taking these factors into account, you can choose the right type of EV charger for your needs and ensure that your vehicle stays charged and ready to go whenever you need it.
- Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between quick and slow EV charging ultimately depends on your specific needs and circumstances. If you need to charge your battery quickly, then quick charging is the way to go. However, if you have more time and want to protect the longevity of your battery, then slow charging may be the better option. It’s important to keep in mind that quick charging can have a negative impact on your battery’s overall health and lifespan, so it’s not recommended to rely on it too frequently. Additionally, it’s important to invest in a high-quality charging station and to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for charging your EV battery. By doing so, you can ensure that your battery stays healthy and performs optimally for years to come. Ultimately, the key is to find a charging routine that works for you and your lifestyle, while also prioritizing the health and longevity of your EV battery.